accuracy of acetabular labrum tear tests trial|acetabular labral tear management : specialty store The objective of the study was to determine diagnostic accuracy and validity of the patient history, physical examination and imaging for the diagnosis of acetabular labral tears in patients presenting with hip pain. 25 de jan. de 2024 · Lyon x Rennes: onde assistir, horário, escalações e estatísticas. Escrito por Luiz Antônio Sotero; Última atualização: 25/01/2024 às ; 11:32. Ficha técnica. Liga 1. 2. . (Lyon x Rennes) Lyon. A equipe vem de vitória sobre o Bergerac Perigord, pelo placar de 2 a 1, em duelo válido pela Copa da França. Les Gones, que ocupam a .
{plog:ftitle_list}
WEB2,5 988 notas, 142 críticas. Adorocinema. 1,5. Meus amigos. --. Acolhido pela filha do faraó ainda bebê, Moisés cresce como príncipe do Egito, mas volta-se contra sua família .
Acetabular labral tears are an area of increasing interest to clinicians involved in the diagnosis of musculoskeletal complaints of the hip. This review systematically evaluated the evidence for .Using arthroscopy as the reference standard, hip labral tears were clinically suspected with 80-85% accuracy. The clinical diagnostic accuracy of the PT, OS, and ORs was high with no . As arthroscopy is an invasive surgery, adjuvant imaging of the acetabular labrum is increasingly imperative for orthopedists to diagnose and assess labral lesions prior to hip .
spring fatigue testing machine
All labral tears were confirmed by arthroscopy, demonstrating that the impingement test is extremely accurate in the diagnosis of labral tears. The McCarthy test for acetabular .The objective of the study was to determine diagnostic accuracy and validity of the patient history, physical examination and imaging for the diagnosis of acetabular labral tears in patients presenting with hip pain.
Arthroscopy remains the reference standard for diagnosing acetabular labral tears allowing for dynamic examination and assessing the extent of the tear [50, 52]. However, it is more . A recently published randomized controlled trial demonstrated that for patients over the age of 40 years, with minimal osteoarthritis and a symptomatic acetabular labral tear, .Methods: In this single-surgeon, parallel randomized controlled trial, patients older than 40 years who had symptomatic, MRI-confirmed labral tears and limited radiographic osteoarthritis .
So far, several studies have assessed sonographic examination for diagnosis of acetabular labral tears, but the validation of this test has been inconsistent [34–41]. Sonographic examination has a lesser diagnostic ability than CTA or MRI/MRA; thus, it is of limited use in clinical practice [34, 35, 41]. CTA is another diagnostic method for .Interpretation: The impingement test is helpful in identifying acetabular labral tears. If this test is negative and if a labral tear is still suspected, ultrasound can reliably diagnose most tears of the acetabular labrum. MR arthrography is indicated in cases where ultrasound is negative, but the patient suffers continued, specific symptoms.
All labral tears were confirmed by arthroscopy, demonstrating that the impingement test is extremely accurate in the diagnosis of labral tears. The McCarthy test for acetabular labral tears 7 was developed earlier than the FADER and FABER tests. Although a positive McCarthy test is not very common in labral lesions, it has a high specificity.acetabular labral tears. Once considered an uncom-mon entity, labral tears as a source of symptoms and functional limitation in the hip region have become more recognized. A labral tear was arthroscopically identified in 90% of individuals with mechanical hip symptoms.29,55 However, isolated labral tears occur inDiagnostic accuracy of clinical tests for the diagnosis of hip femoroacetabular impingement/labral tear: a systematic review with meta-analysis Br J Sports Med . 2015 Jun;49(12):811. doi: 10.1136/bjsports-2014-094302.diagnostic accuracy of the clinical examination measures relative to hip femoroacetabular impingement and labral tear. Screening filters were initially used during assessment of title,
Femoroacetabular impingement. It is unusual for acetabular labral tears to occur in the absence of a bony abnormality 5 and the most common cause is the presence of femoroacetabular impingement. Ganz et al. 6 postulated that with bony incongruity of the femoral head within the acetabulum, abnormal contact between the proximal femur and the .View our orthopaedic doctors who specialize in diagnosing and treating shoulder labral tears. Types of Labral Tears of the Shoulder. There are several areas around the glenoid where a shoulder labral tear can occur: Bankart tear: A Bankart tear or lesion occurs at the front/lower part of the glenoid. Posterior labrum tear: This tear occurs at .
The acetabular labrum is a fibrocartilaginous structure that is triangular in cross-section and attaches to the bony rim of the acetabulum [1–4].The labrum is approximately 2 to 3 mm thick and is wider and thinner anteriorly, and thicker posteriorly [4–7].By providing up to a 21% increase in acetabular depth, the labrum enhances hip joint stability and increases .
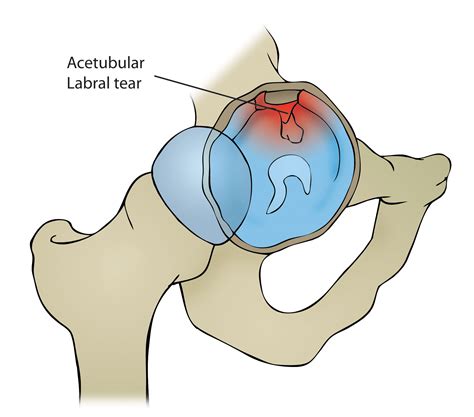
Wang WG, Yue DB, Zhang NF, et al. Clinical diagnosis and arthroscopic treatment of acetabular labral tears. Orthop Surg 2011;3:28–34. Chan YS, Lien LC, Hsu HL, et al. Evaluating hip labral tears using magnetic resonance arthrography: a prospective study comparing hip arthroscopy and magnetic resonance arthrography diagnosis.Diagnosis. Undersurface detachment of the posterior superior right acetabular labrum. Introduction. Although previously thought to be a relatively uncommon injury, acetabular labral tears are becoming diagnosed with increasing frequency because of improvements in MRI and arthroscopic techniques. 1 The prevalence of labral tears in patients with hip or groin pain has .the main reason labral tears occurred (running, twisting, slipping). But with improved radio - graphic imaging and anatomy studies, it s clear now that abnormal shape and structure of the acetabulum, labrum, and/or femoral head can also lead to the problem. Injury is still a major cause for labral tears. Anatomical changes that contribute to labral
Conventional MRI was assessed in 13 studies and MRA was assessed in 16 studies. Whilst both MRI (0.5-3T) and MRA (0.5-3T) presented with a moderate sensitivity and specificity (sensitivity 66%, 87%; specificity 79%, 64%), diagnostic accuracy of MRA appeared to be superior to MRI in detecting acetabular labral tears on ROC curve interpretation. The acetabular labrum is an important structure that contributes to hip joint stability and function. Diagnosing labral tears involves a comprehensive assessment of clinical symptoms, physical examinations, imaging examinations, and arthroscopic confirmation. As arthroscopy is an invasive surgery, adjuvant imaging of the acetabular labrum is increasingly .A randomised controlled trial by Mansell et al. . ↑ Caliesch R, Sattelmayer M, Reichenbach S, Zwahlen M, Hilfiker R. Diagnostic accuracy of clinical tests for cam or pincer morphology in individuals with suspected FAI syndrome: a .
Acetabular labrum tears (labral tears) can cause pain, stiffness, and other disabling symptoms of the hip joint. . Studies show that MRA is highly sensitive and specific for labral tears. This test may replace arthroscopic examination .The acetabular labrum is a soft-tissue structure which lines the acetabular rim of the hip joint. The joint is surrounded by ligaments that work to keep this articulation intact. Movements of this joint are facilitated by the articulation of . Acetabular labral tear, as the name implies, is a tear involving the acetabular labrum of the hip. . most accurate imaging study (91% vs 36% on native MRI) minimally invasive compared with arthroscopy. highly diluted intra-articular Gd-injection (0.0025 mmol/ml) with joint distension (10-20 ml) allows optimal assessment of the labrum on T1 .
acetabular labral tears. Once considered an uncom-mon entity, labral tears as a source of symptoms and functional limitation in the hip region have become more recognized. A labral tear was arthroscopically identified in 90% of individuals with mechanical hip symptoms.29,55 However, isolated labral tears occur in
Our latest blog and tutorial videos offer evidence-based strategies and insights into managing hip labral tears. Learn about the top new tests, treatments, and exercises for optimal outcomes. . might be competing for the title of the “best hip acetabular labral tear test. . A prospective, randomized, controlled trial comparing .Hip labral tears commonly occur between 8 to 72 years of age and on average during the fourth decade of life; Women are more likely to suffer than men; 22-55% of patients with hip or groin pain symptoms are found to have an acetabular labral tear; Up to 74.1% of hip labral tears cannot be attributed to a specific event or cause
A 2009 comprehensive review of hip labral tears by Groh and Herrera states that prevalence of labral tears in those patients with groin or hip pain is 22-55%.2 This same review suggests that labral tears were found more often in younger patients, rather than labral tears in addition to The reader is referenced to that article and is also directed to the article by Burnett et al. , dealing with the history and clinical tests for FAI and labral tears. Having established acetabular causes and regimen of diagnosis, the possibility of cam impingement should be considered as a cause of the pain and its existence established.The acetabular labral tear: an arthroscopic classification. Arthroscopy 1996;12(3):269–272; ↑ Czerny C, Hofmann S, Neuhold A, et al. Lesions of the acetabular labrum: accuracy of MR imaging and MR arthrography in detection and staging. Radiology 1996;200(1):225–230Medical tests will also be done to track the health of participants. . Acetabular labral tears (ALT) have been reported to have a prevalence of 22-55% in patients presenting with hip or groin pain. . or magnetic resonance angiography (MRA), and diagnostic injection. Conservative management trials are often considered for initial treatment .
The prevalence of labral tears among patients with groin pain is classically described as 22–55%, although it is reasonable to expect higher rates in a hip specialist’s practice [9, 10, 14, 15].It is also likely that those rates are currently even higher, in consonance with the exponential growth in hip arthroscopy volume during the last two decades—a reported 25-fold .The FADIR test is commonly used in the assessment of hip pathology, espeially femoroacetabular impingement and labral tear. However, due to high sensitivity and low specificity of the test, it is important to understand its limitations and consider its role in conjunction with other tests and diagnostic tools when assessing hip pathology [1] .
labral tear diagnosis
Viagens. Beto Carrero World: Conheça o maior parque temático da América Latina + 11 atrações. Equipe Império das Milhas 22 de setembro de 2023. O Beto Carrero World é .
accuracy of acetabular labrum tear tests trial|acetabular labral tear management